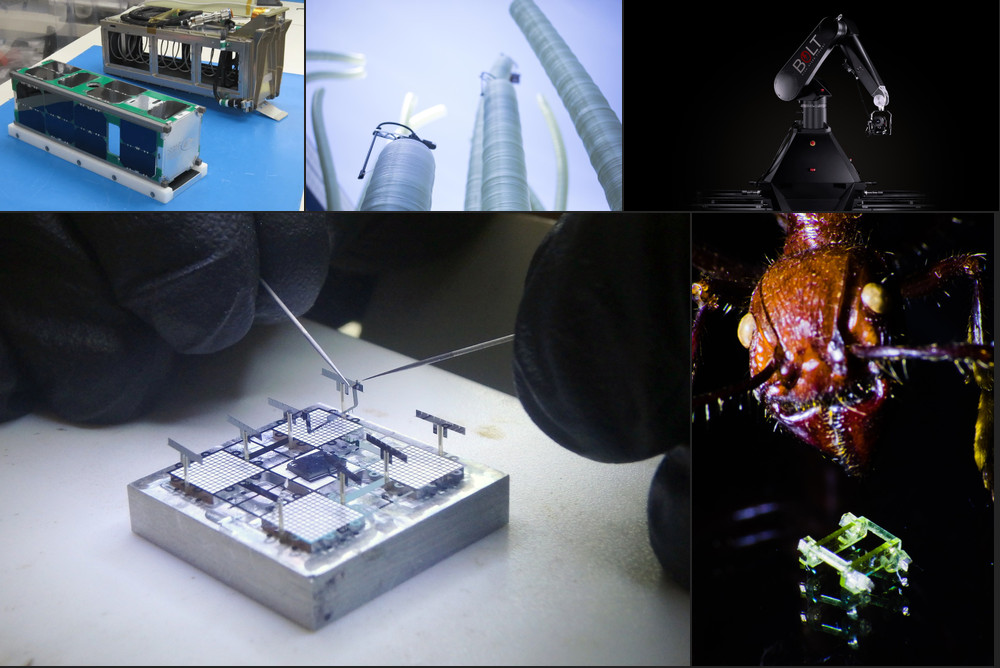
1) An Introduction to Cubesats.
gereshes.com
INFO: This short article is a quick and informative introduction to cubesats. We were surprised to learn that there were instances of cubesats used for deep space missions.
2) FIBERBOTS: Design of a multi-agent, fiber composite digital fabrication system.
MIT
INFO: “The FIBERBOTS are a swarm of robots designed to wind fiberglass filament around themselves to create high-strength tubular structures. These structures can be built in parallel and interwoven to rapidly create architectural structures”. The video contained in the article is well worth the watch.
3) Four-Legged Walking Robot Is Smaller Than an Ant’s Face.
IEEE
INFO: Ryan St. Pierre for University of Maryland designed a quadruped robot that weighs 1 milligram and measures 2.5 mm x 1.6 mm x 0.7 mm. The legs of the robot are controller by external magnetic fields acting on magnets embedded in robot hips. The top speed of the robot is 37.3 mm/s.
4) Penny-Sized Ionocraft Flies With No Moving Parts.
IEEE
INFO: Backin in Weekly Robotics #15 we mentioned a ion drive powered fixed wing aircraft. In the above link a ioncraft developed by UC Berkley researchers is presented. The aircraft measures 2 cm x 2 cm and together with IMU weighs 67 milligrams. To be able to hover the robot requires an input voltage of 2,000 V at 0.35 mA.
5) Bolt - High Speed Cinebot.
Mark Roberts motion Control
INFO: The other day we’ve enjoyed learning about this robot arm cameraman. The website above contains showreels showing the robot in action and you will also find the relevant datasheets in case you are interested in physical characteristics of this arm.
6) MIT Robot Combines Vision and Touch to Learn the Game of Jenga.
MIT
INFO: MIT Engineers developed a tactile sensing system that enables an ABB IRB 120 robotic arm to engage in a game of Jenga. To determine how to move a block the robot uses both vision methods and force measurements. You can see the robot in action by watching this video.
7) Publication of the week - How Many Miles of Driving Would It Take to Demonstrate Autonomous Vehicle Reliability (2016)?
RAND Corporation
INFO: This paper discusses using test-driving as a safety metric in autonomous vehicles. According to authors to statistically demonstrate reliability the autonomous cars would need to drive between tens of millions to hundreds of billions miles depending on chosen benchmark.
Careers
0) Would you like to advertise an open position in a robotics related company?
Weekly Robotics
INFO: If you would like us to include your open position in the hiring section please feel free to send us an e-mail.
1) Stanley Robotics (Paris, France) - Various Positions.
INFO: Stanley Robotics is the company behind the autonomous parking robots that we covered in WeeklyRobotics #24.
2) Auterion (Zurich, Switzerland / US) - Various Positions.
INFO: Auterion builds the tests, certified, and long-term supported distribution of PX4 for the safe operation of autonomous robots.
3) Automata (London, UK) - Various Positions.
INFO: Automata is a startup building small robot arms for manufacturing and logistics.
